Content Strategy
Content strategy focuses on the planning, creation, delivery, and governance of content. Content not only includes the words on the page but also the images and multimedia that are used. Ensuring that you have useful and usable content, that is well structured, and easily found is vital to improving the user experience of a website.
Creating a Strategy
The goal of content strategy is to create meaningful, cohesive, engaging, and sustainable content. A contentstrategy helps you to identify what already exists, what should be created and, more importantly, why it should be created.
Content-oriented Components
- Identify Goals and Substance: focuses on what content is required to successfully execute your core strategy. It includes characteristics such as messaging architecture, intended audience(s), and voice and tone.
- Determine Structure: focuses on how content is prioritized, organized, and accessed. Focuses on the content itself, including mapping messages to content, content bridging, and creating detailed page tables.
People-oriented Components
- Outline the Roles and Workflow: focuses on how people manage and maintain content on a daily basis, including the roles, tasks, and tools required throughout the content lifecycle.
- Identify Policies and Standards: focuses on the policies, standards, and guidelines that apply to content and its lifecycle, as well as how an organization will sustain and evolve its content strategy.
Content Lifecycle
Producing compelling and sustainable content means that you need to understand and follow the content lifecycle.
- Audit and Analysis: Content stakeholder interviews, competitive analysis, objective analysis and evaluation of the content environment (site, partner content, sister, parent sites)
- Strategy: Determine topical ownership areas, taxonomy, process/workflow for content production, sourcing plan, voice and brand definition
- Plan: Staffing recommendations, content management system customization, metadata plan, communications plan, migration plan
- Create: Writing content, asset production, governance model, search engine optimization, quality assurance
- Maintain: Plan for periodic auditing and determine targets for success measures.
Instead of thinking of who owns each deliverable, it’s important to think of who contributes to each and how those different contributions come together to define the final product. There’s value in including multiple perspectives on deliverables.
Content Best Practices
Each piece of content should abid by the following:
- Reflect your organization’s goals and user’s needs. You can discover your user’s needs through conducting market research, user research, and analyzing web metrics.
- Understand how user’s think and speak about a subject. Content should then be created and structured based on that. Doing this will also help you with search engine optimization (SEO).
- Communicate to people in a way that they understand. Embracing plain writing principles helps with this.
- Be useful. By being purposeful in the content that you include, omit the needless.
- Stay up-to-date and remain factual. When new information becomes available, update your content or archive it.
- Be accessible to all people. You have a responsibility to make sure that all people can access and benefit from your information.
- Be consistent. Following style guides, both for language and design, helps people understand and learn what you are trying to communicate.
- Be able to be found. Make sure that users can find your content both through internally through navigation and also externally through search engines.
- Help define the requirements for the overall site. Content should drive design, structure, etc
SEO Checklist
This checklist is assuming that all keyword research has previously been completed.Here is a step-bystep guide on how to research keywords.
1. Title Tags
The title tag tells search engines what the page is about and that the page on your website is relevant for that keyword or keyword phrase. Title tags should be unique for every page. In search results, search engines will highlight your keyword phrases if a user has searched for those terms. This increases visibility and click-through rate.
Best Practices:
- Your title tag should be written like this: Primary Keyword – Secondary Keyword | Brand Name
- Use a dash in between your keyword phrases and a pipe at the end before your brand name
- Avoid duplicate title tags
- Keep title tags at 55 characters or less in length, including spaces.
Example:
Example of title tag represented in the browser:
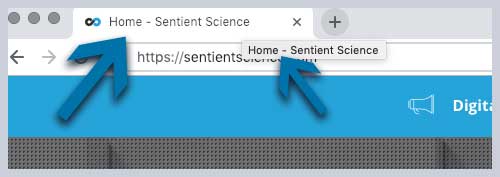
Example of title tag in the search engine results:

2. Meta Descriptions
Meta descriptions, while not as important in search engine rankings, are extremely important in getting users to click through from the search engine results page (SERP) to your website. Meta descriptions should use keywords wisely, but more importantly they should include a compelling description on which a user would want to click on.
Much like title tags, the SERPs will highlight keywords that the user searched for, increasing the likelihood of the user clicking through to your website.
Best Practices:
- Write compelling meta descriptions
- 150 to 160 characters is the recommended length
- Avoid duplicate meta descriptions
- Do not use quotes or any non-alpha characters (Google, cuts them out of the meta description)
Example:

3. Content with Targeted Keyword Phrases
Content is King! With all of the Google Panda updates, it is extremely important that your content is unique and relevant. If you have multiple pages with the same content (or if you have your content on other people’s websites), you will run the risk of getting penalized by Google and your search rankings will suffer.
Best Practices:
- Create content that is extremely relevant for that keyword phrase
- Use your keyword phrase 4 times within your content
- Include links from other pages within your website that point back to this page
- Create unique content for every medium. For example, if you send out a press release, do not copy and paste that press release onto your website. If it gets picked up in multiple publications, the search engines will see that you have duplicate content and penalize you for it.
4. Header Tags and Keyword Phrases
A header tag, also known as an H1 tag, is much like the subject line of your web page. You should only use your keyword phrase once in the H1 tag. This should be included on a page to which you are trying to drive unique traffic to. You can also use H2 tags (second header) if there are multiple sections.
Best Practices:
- Use your keyword phrase once in your H1 tag
- Use H1 tags on pages you are trying to drive unique traffic to (SEO page)
- Use H2 tags if there are multiple sections
Example:

Example of the page header, the h1 tag, being optimized for the keywords.
5. Internal Page Linking with Anchor Text
Internal linking refers to a link on a page that points to another page on the same website. Internal linking is important because it helps strengthen those keywords internally for those pages, it allows users (and search engine robots) to navigate through the website, and it tells the search engines that the page is relevant for that keyword phrase.
Best Practice:
When linking to another page on the same site from within content, select good anchor text (keywords) to use in the actual link and do this often.
Example:
“We offer a wide range of web design services,” rather than “Click here for our services.”
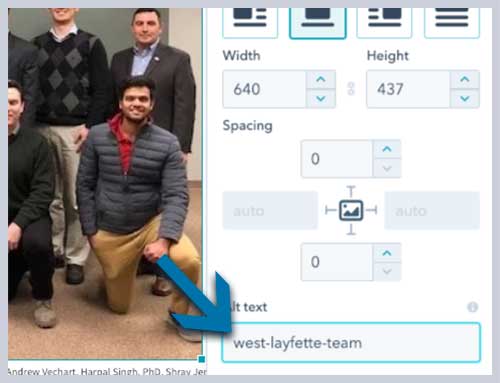
6. Image ALT Tags and Filenames
An ALT tag is essentially the name of an image. All images should use appropriate ALT tags. Not only are ALT tags good for search engines; they are also good for accessibility. If someone is using a screen reader, they will be able to hear what that image is.
You should try to include your keyword phrase in the name of your image, if possible, but don’t overdo it. Image filenames should also be SEO friendly. Image search is much more widely used than believed, so traffic from there is also valuable.
Best Practices:
- Name all of your images in a way that describes what they are
- Use dashes between the words, rather than underscores ( purple-hat.jpg rather than purple_hat.jpg)
- Do not use non-alpha characters in your image or file names (so no %, &, $, etc…)
Example:
7. Make Content Easy to Read
This is not a huge factor in search engine rankings, but will help your users easily scan your content and find the keywords they are looking for. You should use bolding and bullet points to set apart words in the text, and this further tells the engines what is important on the page. Don’t go wild or you’ll end up cluttering up your page and aggravating the user.
Best Practices:
- Paragraphs should be roughly three sentences long. Extremely long sentences will lose the users’ attention
- Use bullet points and bolding to break up large blocks of content. Users tend to scan content looking for keywords
- Do not overuse bullets and bolding